Overview
A primary objective of the Business Payments Coalition (BPC) is to promote digitalization and straight-through processing (STP) of electronic payments between businesses. Key activities to support that objective are to catalyze widespread adoption of electronic invoices (e-invoices), and automated processing of remittance data (e-remittance). In addition, the BPC supports adoption of the ISO 20022 payment message standard as one key ingredient to achieve operational efficiencies, improvements to treasury management and customer experience, and improved global interoperability.
As part of its efforts to modernize business-to-business (B2B) payments, the BPC aims to support the industry’s migration from checks to electronic payments. Electronic payments allow for businesses to take advantage of the benefits that digitalization brings, including lower costs, better cash management, error reduction, risk mitigation, increased transparency and improved automation for business processes.
The Power of an Exchange Framework
One of the key steps to achieving ubiquitous B2B electronic payments in the United States is establishing a standard way to send electronic invoices (e-invoices) and remittance (e-remittance) data between businesses. An exchange framework is an electronic delivery network based on a set of technical standards and policies to allow businesses to securely share electronic supply chain documents with one another. An exchange framework, allows for improved payments efficiency by transforming B2B invoicing and remittance information processes from a fragmented, manual, multi-step process to an automated one that, ideally, achieves straight-through processing.
In an exchange network, service providers act as access points to deliver and receive data and information for their business clients. The virtual network allows access points to find and connect business end points while preserving client confidentiality. In an ideal state for B2B payments, these exchanges will support both invoices and payment remittance information and enable straight-through processing of both.
The infographic below details how exchange frameworks allow for the widespread exchange of e-invoice and remittance data.
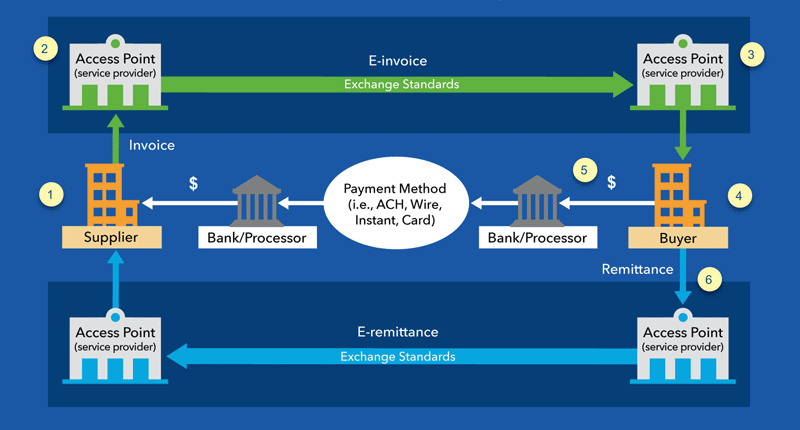
First, a supplier (1) engages with their e-invoice provider, or access point (2). The supplier issues the invoice and sends it to the access point in the format their systems currently support. The supplier’s access point transforms the invoice into an exchange standard format and delivers the invoice to the buyer’s access point (3). The buyer’s access point then converts the invoice to the buyer’s required format and sends it to the buyer (4).
The buyer then processes the invoice and pays using whichever payment type they prefer, including ACH, wire, instant or card payment (5). The supplier then receives the payment through their bank/processor and the transaction is complete.
The remittance information can be sent through a parallel set of access points in the same way as invoices (6).
These virtual exchange networks are frictionless for both the supplier and buyer. They support all payment types and address two of the most challenging inefficiencies for electronic payments – manual processing of invoices and remittance information.
Originally developed and tested by the BPC’s E-invoice Exchange Market Pilot, in the early summer of 2023, pilot participants formed the Digital Business Networks Alliance (DBNAlliance) (Off-site) as the legal entity overseeing the exchange framework. DBNAlliance assists service providers to connect to the exchange framework and is responsible for defining electronic delivery standards, policies, rules and guidelines for e-invoicing. Furthermore, DBNAlliance will govern the exchange framework that is available to all businesses via their service providers.
Learn more about the Digital Business Networks Alliance (Off-site) and how you can connect by contacting them here: membership@dbnalliance.org.
Resources
- SMB Accounting Software APIs Initiative (PDF) (2019)
This paper documents the work of the BPC to research Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) available to facilitate electronic payments in small-to-medium business accounting software. - Retail Debit Balances Best Practices and Procedures (PDF) (2016)
This Technical Report offers best practices and procedures for standardizing the handling of debit balances from both the supplier and retailer perspectives. The scope includes account reconciliation, notification guidelines, timeframes, roles and responsibilities of each party, and supporting documentation. - Best Practices for Handling Retail Debit Balances Webinar Recording (YouTube) (2016)
This technical report is a useful tool for retail industry members and software vendors who desire to improve and standardize how debit balances are handled by various trading partners.
- B2B Directory Concept Paper (PDF) (2014)
2014 whitepaper from the B2B Directory workgroup documenting the directory concept - Survey of Business Practitioners – Final Report (PDF) (2012)
Summary of results of the 2012 survey of business practitioners about Electronic Payments & Remittance Data: Pain Points & Solutions